Domain-Driven Design
Domain-Driven Design (DDD) is a software development approach that focuses on generating a deep understanding of the business domain. It is a way of thinking and a set of priorities, aimed at accelerating software projects that have to deal with complex domains.
Key concepts
- Ubiquitous language: The language is used by all team members, from
product owners, to developers, QA, and stakeholders. Business concepts, rules,
entities, and processes are described using this common language to ensure
clear communication and understanding. For example, using terms like
Invoice,Payment, andCustomerconsistently across documentation and code. - Domain model: An abstract representation of the business domain that
captures its key concepts, relationships, and behaviors. The domain model is
expressed using the ubiquitous language and serves as a blueprint for the
software design. For example, in an e-commerce application, the domain model
may include entities like
Customer,Order, andProduct, along with their relationships and behaviors. - Entities: Objects that have a distinct identity that even if all
attributes change, the identity remains the same. For example, a
Customerwith a unique ID. - Value objects: Objects that are defined by their attributes rather than a
unique identity. They are immutable and interchangeable when their attributes
are the same. For example, a
Moneyobject with attributes like amount and currency. Usually, used as invariants. - Aggregates: A cluster of related entities and value objects that are
treated as a single unit for data changes. Aggregate have a root entity which
is responsible for maintaining the integrity of the entire aggregate. For
example, an
Order(root) aggregate may consist ofOrderItementities and aShippingAddressvalue object. - Repositories: interfaces that provide methods for managing the persistence
of aggregates. Implementation is done in the infrastructure layer. For
example, a
CustomerRepositoryinterface may provide methods to add, remove, and find customers. - Bounded context: A defined boundary within which a specific domain model
is valid. Different bounded contexts may have different models and ubiquitous
languages, even if they are part of the same overall system. For example, in a
large e-commerce platform, the
Inventorybounded context may have its own model and language that is distinct from theSalesbounded context. - Invariant: is a business rule that must always be true so the data is considered valid.
- Domain Events: Important occurrences within the domain that are of
interest to the business. They represent state changes or important actions
that have taken place. For example, an
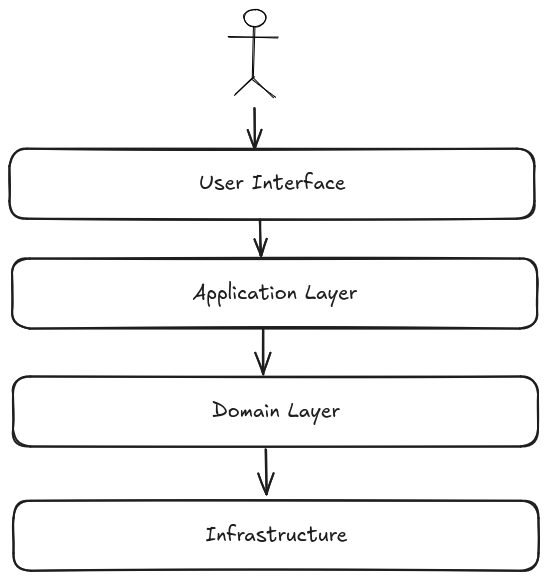
OrderPlacedevent may be triggered when a customer places an order and can be used to notify other parts of the system. - Layers: DDD can be implemented in layers, in a hexagonal
architecture, where the domain model is at the
center of the architecture. The common layers are:
- Presentation layer: The user interface, responsible to interact with the application or user.
- Application layer: orchestrates the domain objects to perform the required operations or use cases.
- Domain layer: The core of the application, where the business logic resides.
- Infrastructure layer: The external systems that the application interacts with, like persistence, messaging, etc.